RAG Roadblocks and Evaluation Strategies
The next topic was covered greatly and in more detail in this YouTube live session. This is my own interpretation on what was discussed there.
2023 will probably be remembered as the year of the big boom of Generative AI prototypes. As 2024 unfolds, the market is shifting towards production and deployment, but there are significant issues with LLMs, such as hallucinations caused by factual inconsistencies and fabrications, opacity in the data used to train the models, and the inability to leverage proprietary information to provide content.
RAG have gained traction in reducing the gap between the development and deployment of LLM prototypes. This approach stands out for its cost-effectiveness and potency in creating applications. RAG offers a unique and cost-effective yet powerful way to take advantage of utilizing proprietary data without the need for extensive model fine-tuning.
Where can a RAG system go wrong?
- Input Data:
- Do you have sufficient data?
- Is it properly labeled?
- Is the quality high?
- Chunking strategies:
- Are you employing the correct chunk size?
- Embedding Space:
- Are you optimizing your embedding parameters?
- Vector Store:
- Is the retriever retrieving the appropriate chunks of data?
- Do these chunks truly contribute to solving the response, or not?
- It is possible that the retriever is not selecting the right pieces of information.
- Are all the relevant chunks used, or is there a low utilization of other pertinent chunks? How much of each chunk is being utilized to answer the question?
- Is the prompt constructed properly, capturing both the question and context for a proper response?
- What portion of the chunks is used to generate a response from the model?
- Output:
- Does the model response adhere to the prompt and provided query, or is it hallucinating and providing undesired information?
- To what extent did the model address the user’s question?
- Does the model output comprehensively answer the initial query, or is the response incomplete, resulting in a poor-quality output?
Problem and Roadblock:
Products often get stuck in the prototype phase, primarily due to challenges in evaluating RAG. Evaluation poses the most significant roadblock on the path to production. For the high-quality development of applications, it is crucial to conduct evaluations and experiments across the RAG stack. Having quantifiable metrics is important to illuminate these issues.
What is the desired performance?
We aim for the input to be minimal and accurate, seeking dense information just enough to generate a high-quality output. The desired output from your system is to formulate an answer that thoroughly addresses the question asked, maintaining accuracy and relevance to the context.
RAG evaluation
How can we evaluate the performance and take actions to improve it?
Output Quality:
Context Adherence: To what extent does the output align with the syllabus? Objective is to avoid hallucination.
Completeness: Ensure key information is not omitted from the answer. Assess the comprehensiveness of the output.
Retrieval Strategy:
Chunk Utilization: Evaluate intra-chunk utilization. Examine if the response uses all the relevant section of the context.
Chunk Attribution: Aim for a high number of relevant chunks used, ensuring the response includes all pertinent chunks.
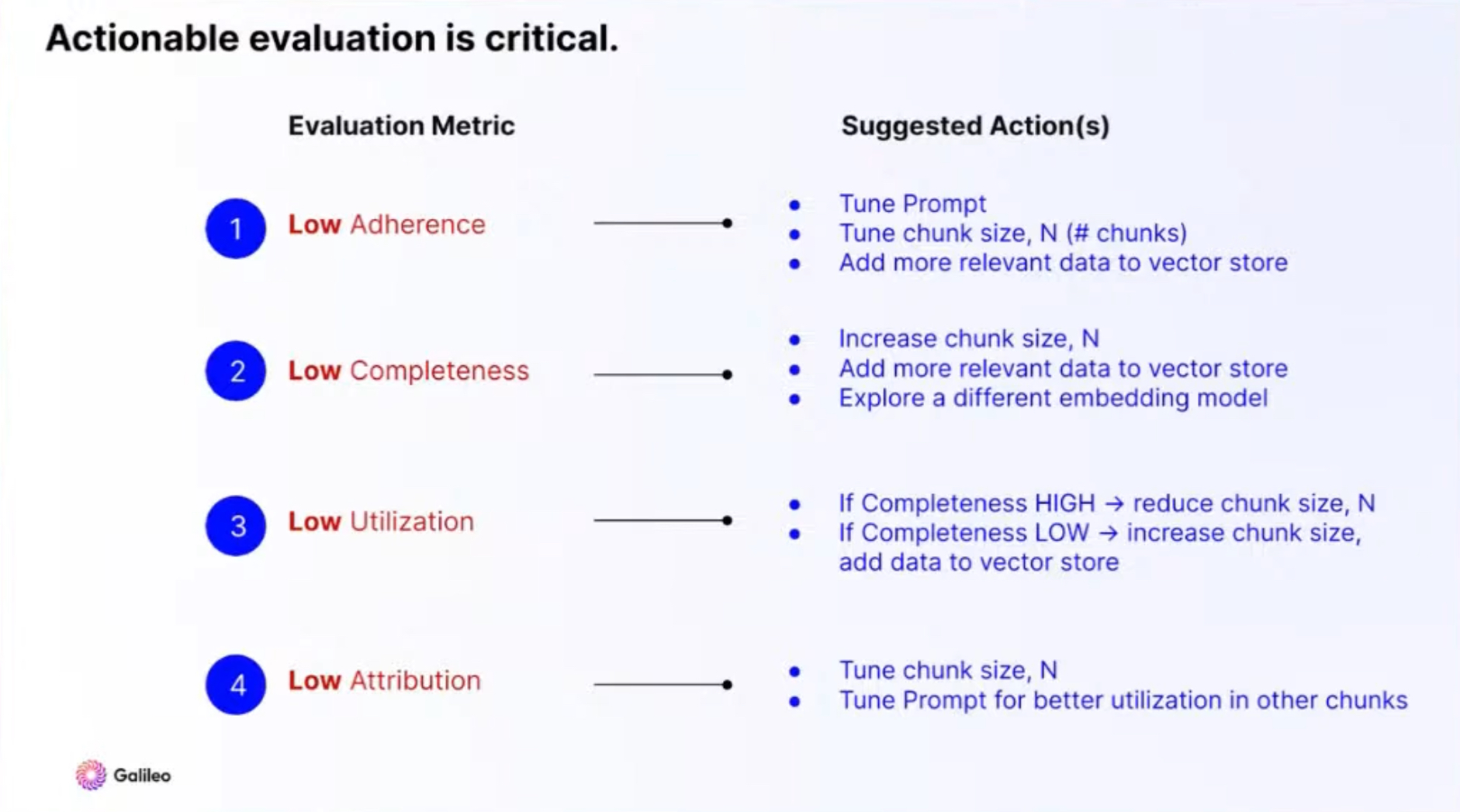 Actionable Evaluation. Source: Galileo
Actionable Evaluation. Source: Galileo